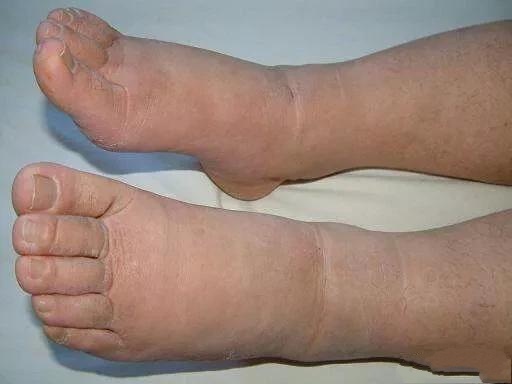
Foot swelling in a 90-year-old individual can be due to various causes, including heart failure, kidney disease, or venous insufficiency. Treatment should be tailored to the underlying cause. Here are some general steps:
1. Medical Evaluation: First, a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to determine the cause of the swelling. This may involve blood tests, imaging studies, or other diagnostic procedures.
2. Addressing the Underlying Cause: Treatment will depend on the underlying cause. For heart failure, medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or beta-blockers may be prescribed. Kidney issues may require adjustments in fluid intake or dialysis. Venous insufficiency may be managed with compression stockings or, in severe cases, surgery.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Reducing salt intake, staying hydrated, and elevating the legs when sitting or lying down can help reduce swelling.
4. Physical Activity: Gentle exercise, such as walking or leg raises, can improve circulation and help reduce swelling.
5. Medication: In some cases, medication may be necessary to help manage the swelling. Diuretics, for example, can help the body eliminate excess fluid.
6. Regular Monitoring: Close monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential to adjust treatments as needed and to watch for potential complications.
It's important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive management plan tailored to the elderly individual's specific needs and the underlying cause of the foot swelling.











